Duet 3 Mini 5+ with Canbus boards.
-
@droftarts said in Duet 3 Mini 5+ with Canbus boards.:
Try connecting the CAN wires the other way around. Probably easiest to switch them at the Mini 5+ end.
Wow, really? Perhaps a wiring diagram for the whole setup? Am I asking too much?
I saw absolutely nothing in your documentation about wiring High to Low."The Tool Distribution board isn't hard to understand; CAN1_H and CAN1_L connect to the TDB from CAN IN to, initially, Tool 0 connector. It goes out to a toolboard using the Tool 1 pins 3 and 4, and comes back in on pins 1 and 2. These are named CAN_H_0-1 and CAN_L_0-1, to show they connect from tool 0 to tool 1. This is done internally, to pins 4 and 3 of the Tool 1 connector. And so on, to Tool 2 and 3, and to CAN OUT. This keeps the CAN wires as a continuous bus, without the CAN_L or CAN_H wires crossing over, except at the ends of the bus, where it's terminated. You can see this in the wiring schematic:"
If you can parse this into a functional wiring setup, that's great. I, however, cannot. My head is spinning.
Schematic of the wiring, please. I really don't think this is an unreasonable request. Look at what LGO and Bigtreetech are doing with their Type C connector toolboards. If you don't get your setup documented better, they will eat your lunch.
I talked to about 20 people at MRRF about Canbus, they all said it was a pain. Bill Steele, who is a very talented engineer said the only way he could get his working was with an oscilloscope. He told me not only was the i/o and address setup a problem, but that the boards he used had different i/o speeds, which he only detected with the oscilloscope. These were your boards.
-
I saw absolutely nothing in your documentation about wiring High to Low.
No, CAN_H goes to CAN_H, CAN_L to CAN_L. If you have just a Roto and Mini 5+, maybe you got them mixed up. It's easy enough to switch it over.
Perhaps a wiring diagram for the whole setup?
From https://docs.duet3d.com/Duet3D_hardware/Duet_3_family/Duet_3_Roto_Toolboard#can-connection
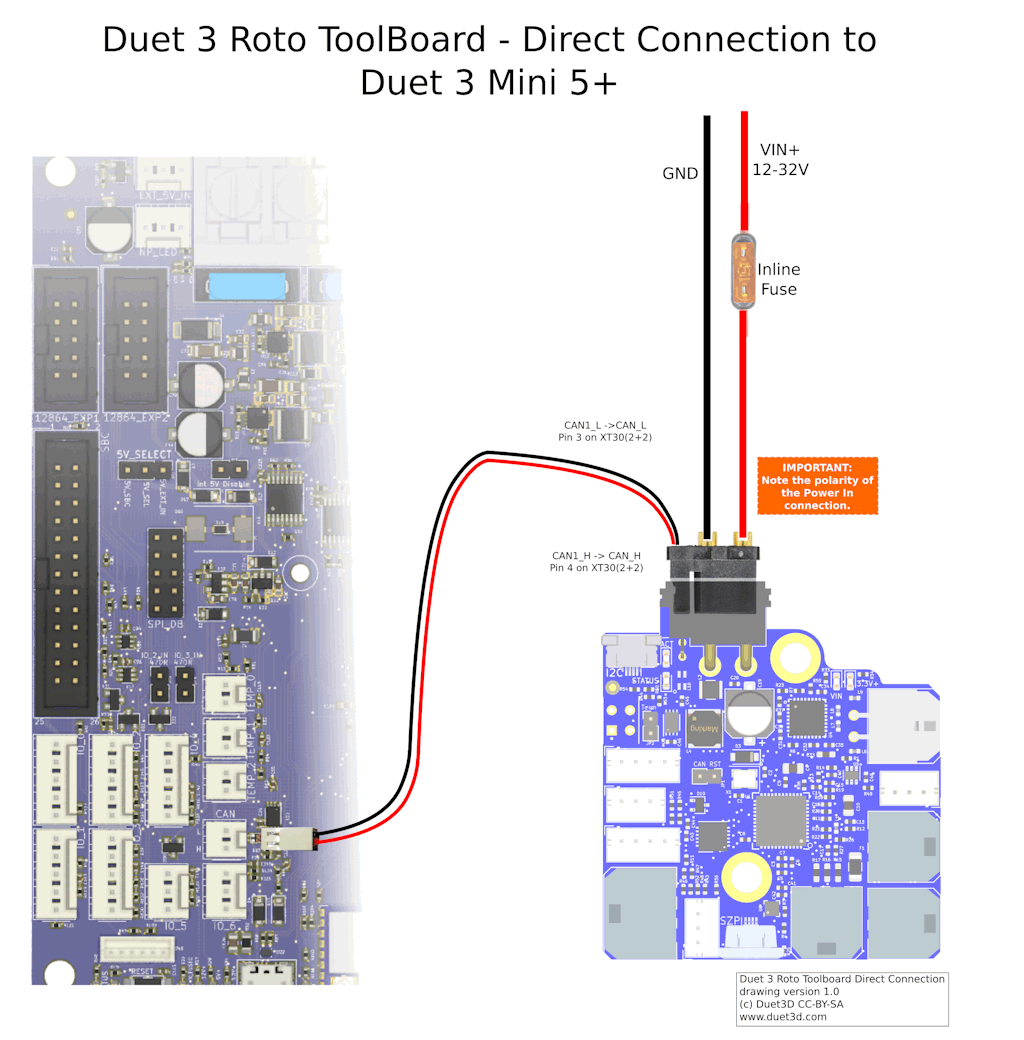
Schematic of the wiring, please.
Ian
-
@droftarts I wired it as shown.
Here is a video:
https://youtu.be/Q99Rn5CfPhk -
@droftarts I found the problem, the Roto Toolboard connector was approx. 0.2mm out of the socket. You can see in the video how very slightly it was out. This killed the L connection, the H was still made. Perhaps a locking Molex plug like the other connectors on this board is called for. Hot glue for the win.
I am still requesting a wiring diagram of the main board/canbus expansion/and 1, 2, 3, or 4 tool board options, with wiring diagrams, bypass jumper, and terminator jumper setups for all 4 options. ANYBODY purchasing your boards who is not familiar with Canbus FD will need this documentation. Thanks.
-
@droftarts Here is a screengrab closeup of the disconnected canbus connector on the toolboard.
I measured it, it is 0.2mm out. Might need a better connector for this.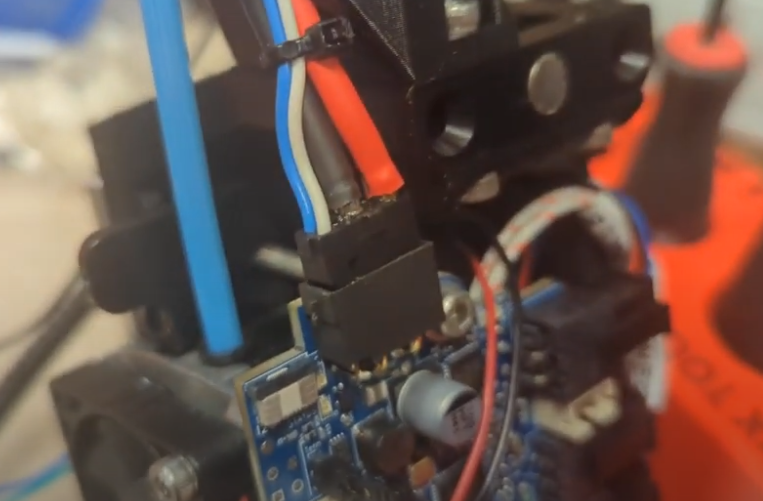
-
@j-pickens That looks like the wiring that came with the very early/prototype Roto boards. We now supply a cable with a moulded plug. I've used both the moulded plug version and the earlier 'open' cable with yellow and white wires, and haven't had any issue with those. Check you plug and socket on the Roto board for damage, debris, mis-aligned pins or crimps not fully engaged in the connector or cable.
I'll draw the Tool Distribution Board wiring today, but it doesn't need four different diagrams. The wiring and function of each Tool connector is the same:
- either the bypass jumpers are not fitted, and you have a tool board like the 1LC (with a 4-pin connector) with a pair of CAN wires going out from the connector, and a pair of CAN wires back to the connector
- or the bypass jumpers are fitted, and
- the Tool connector is either not used,
- or one or two stubs can be connected to either or both CAN_H/L pair.
Termination can either be done on the TDB with the jumper, or on the last toolboard in the CAN bus chain.
I talked to about 20 people at MRRF about Canbus, they all said it was a pain.
I've found the Duet implementation quite the opposite (the Klipper implementation is much more time consuming), so long as you're careful with the wiring.
It's a shame we can't do polls on the forumI've created a poll, as I'd like to see how many people thought it was difficult. Sure, for large systems with lots of boards there's a few hoops to jump through. But it's not like we reinvented the wheel. CAN and CAN-FD have wide usage across multiple industry sectors, and is a robust data transfer bus standard. I feel our documentation largely does a good job of covering it, and we're always improving it. For more advanced issues, there's this forum.Bill Steele, who is a very talented engineer said the only way he could get his working was with an oscilloscope. He told me not only was the i/o and address setup a problem, but that the boards he used had different i/o speeds, which he only detected with the oscilloscope. These were your boards.
Unless the boards are running wildly different firmware versions (and even then I'm not sure it would matter), I don't see how this could possibly be the case. The whole point is that they synchonise when connected. Sure, if you test each board in isolation, the onboard oscillator probably has some variance. But when connected to a mainboard, they sync, and the timing is inherited from the mainboard. Setting the address on boards is also clearly documented, eg https://docs.duet3d.com/Duet3D_hardware/Duet_3_family/Duet_3_Roto_Toolboard#set-the-can-address.
If they are running very different firmware, usually a 'factory reset' will get the board talking and flash compatible firmware. See https://docs.duet3d.com/en/User_manual/Machine_configuration/CAN_connection#factory-resetting-a-tool-or-expansion-board
Another possible issue is if you're powering the expansion board from a different PSU than the mainboard. This can cause a potential difference across the CAN bus, interfering with the signal. We recommend connecting the negative terminals of the power supplies together so they share a common ground, to negate this. See https://docs.duet3d.com/en/User_manual/Machine_configuration/CAN_connection#power-wiring
It is also possible to change the CAN frequency, with M952. How to do this is documented in the Gcode entry.
Ian
-
@droftarts Thank you very much for this response. Looking forward to the wiring diagram.
-
@j-pickens I've done this today. Hopefully it shows how the CAN bus is routed through the board. I'll do diagrams for 2-wire connections tomorrow.
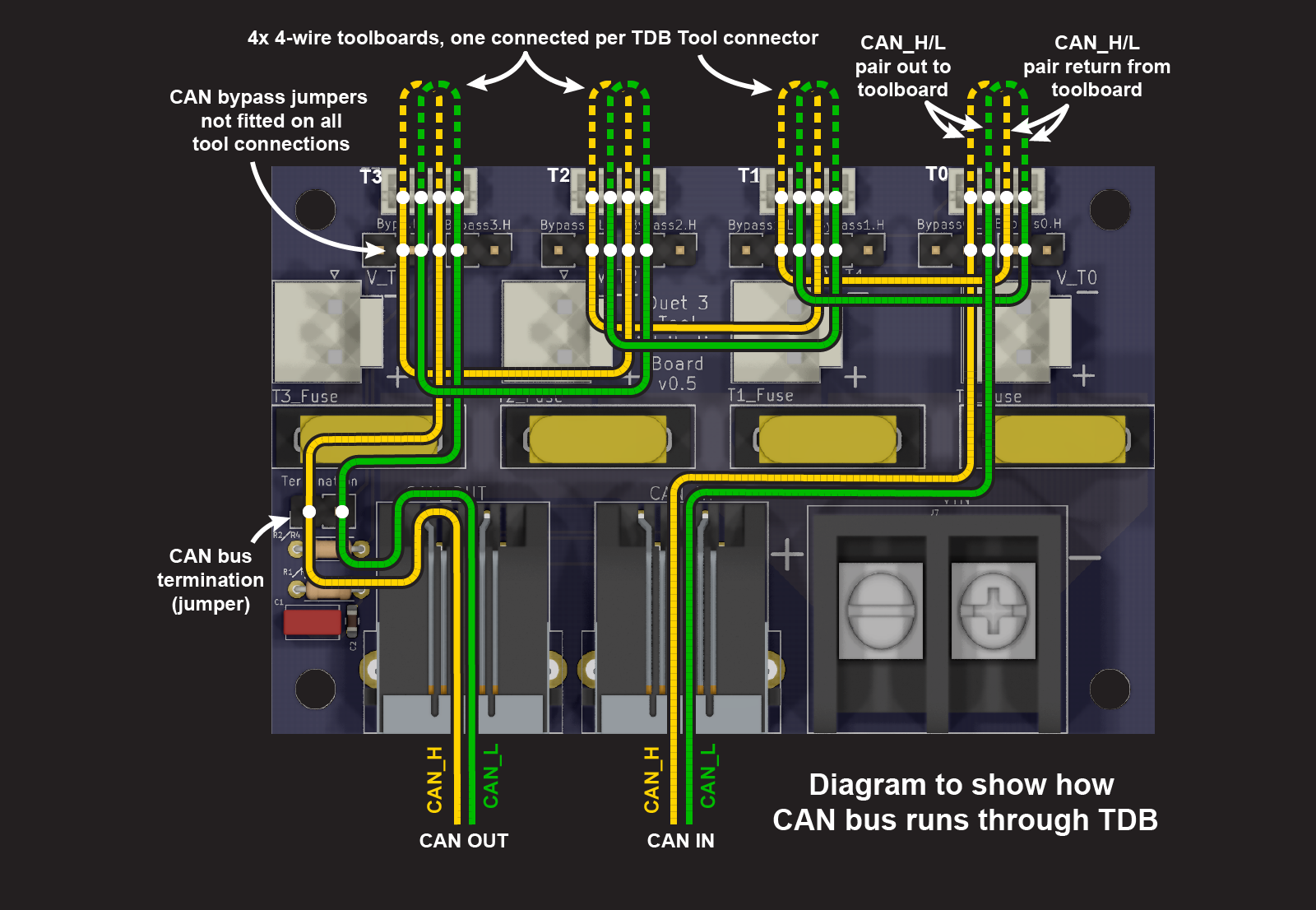
Ian
-
@droftarts This is excellent. Of course, I need the 2 wire Can-FD, so tomorrow it is! I'll attempt a diagram tonight to see how close I get.
-
@droftarts How's your drawing coming? It looks to me like the only way to get the 2 wire signal from the T0 to T1 connector and so on is to use the bypass jumpers. To get T0 pins 1 and 2 to T1 pins 3 and 4. Or remove the jumpers? Not sure. I'll Ohm out these pins and see what is connected with the jumpers in and out.
-
@j-pickens said in Duet 3 Mini 5+ with Canbus boards.:
How's your drawing coming?
Slowly! I only want to do it once, so it necessitates a lot of checking. There's also quite a few variations. Here's what the 4-wire connection to a 1LC currently looks like:
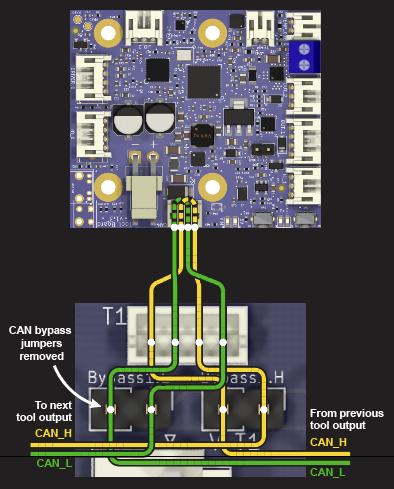
A 1LC can also be connected using 2-wire configuration. As a stub, without termination.
It looks to me like the only way to get the 2 wire signal from the T0 to T1 connector and so on is to use the bypass jumpers.
Correct. That's what I said earlier:
or the bypass jumpers are fitted, and
- the Tool connector is either not used,
- or one or two stubs can be connected to either or both CAN_H/L pair
By 'stubs' I mean a 2-wire connection to a toolboard.
Did you check your Tool Distribution board for solder bridges?
Ian
-
@droftarts So, all bypass jumpers should be in place, and all toolboards should be wired to pins 3 and 4 on each T0-T3 connector. Pin 3 Low and Pin 4 High.
-
@j-pickens Yes. You can actually wire the toolboards to either pair of the tool connector, ie 1 and 2, or 3 and 4. Electrically it shouldn't matter which pair of pins you use. This also means you can wire two toolboards to each connector, one on each pair of the tool connector. I haven't actually been able to test this, but can't see any reason why it shouldn't, so it would be good to check it works. Make sure all 2-wire connections are each under 1m long.
Ian