stepper precision
-
@alankilian said in stepper precision:
bellows coupling
I ordered new couplings but not sure if they would arrive before I need to return the encoder. bellows coupling actually ring more than painters tape, painters tape is very stiff, it behaves for this type of testing (no load!! only the very low inertia of the encoder) perfect. For e.g. I'm not able to move a shaft without encoder catching and a very fast stop (pliers) and no ringing on the encoder... anyhow running multiple turns you see it's pretty repeatable even tape
-
Try gathering data for one-turn slowly clockwise and one turn slowly counterclockwise.
If the data is within your error expectations, you have a good system.
I predict (and I may well be wrong) when you compare those two datasets you will see great variation from one to another and that tells you that your measurements are as accurate as the difference between those to readings.
Another test is to move 180-degrees, take a reading, move 180-degrees the other direction, take a reading and do that back-and-forth movement/reading for many samples.
When you compare multiple reading at the same step location, you will see variation. This also is a measurement of the variation in your measuring setup.
-
@alankilian said in stepper precision:
Try gathering data for one-turn slowly clockwise and one turn slowly counterclockwise.
already done
 the data is spot on, +-0.0
the data is spot on, +-0.0  comparing directions
comparing directions -
What's the angular resolution if your encoder?
-
@alankilian 360/65535 degrees
-
Well, all I can say is you are getting results that do not match with my experience in such situations.
Being able to rotate 180-degrees and repeatable read within 0.005-degree is some kind of black magic indeed. You are a master.
-
@alankilian said in stepper precision:
Well, all I can say is you are getting results that do not match with my experience in such situations.
Being able to rotate 180-degrees and repeatable read within 0.005-degree is some kind of black magic indeed. You are a master.
 we'll see how it goes on the "bigger sample" I just let it go 400 steps forwards and 400 steps backwards and store all the data and spit out differences... would be much easier if I knew python (darn thing don't even have proper arrays) ... as for 180degrees back forth that one I did not test ... I just let it run 3200 steps forward and 3200 steps backwards and compared two greps ... let's see how the aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa sh%$#%^# forgot to pipe it into file
we'll see how it goes on the "bigger sample" I just let it go 400 steps forwards and 400 steps backwards and store all the data and spit out differences... would be much easier if I knew python (darn thing don't even have proper arrays) ... as for 180degrees back forth that one I did not test ... I just let it run 3200 steps forward and 3200 steps backwards and compared two greps ... let's see how the aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa sh%$#%^# forgot to pipe it into file  .. need to run it again ... brb
.. need to run it again ... brb -
@arhi As to your comment about array in python: the numpy package is the default scientific array package. It is a lot like matlab. It is extraordinarily powerful. The python 'array' class, and python's own lists and tuples, are for entirely different purposes than handling what you want.
-
@mendenmh I don't plan to learn python and it's libraries today (I hope never), dunno why it was invented and how the hack it gained popularity but... I'll make it work somehow to get this done.... anyone want to send some code for me to run I'll be happy to
 .. my example that's attached is enough for anyone to know how to read the data from encoder and move the motor, so I'll run the code provided and report back results
.. my example that's attached is enough for anyone to know how to read the data from encoder and move the motor, so I'll run the code provided and report back results  if anyone is interested ...
if anyone is interested ...attm waiting for this to finish:
#!/usr/bin/env python3 import pyprofibus import time import RPi.GPIO as GPIO def main(watchdog=None): master = None forwarddata = [] backwardsdata = [] #poserem se na jezik for i in range(410): forwarddata.append(0); backwardsdata.append(0); try: config = pyprofibus.PbConf.fromFile("arhi_readencoder.conf") master = config.makeDPM() outData = {} for slaveConf in config.slaveConfs: slaveDesc = slaveConf.makeDpSlaveDesc() master.addSlave(slaveDesc) outData[slaveDesc.slaveAddr] = bytearray((0x00, )) master.initialize() GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BCM) GPIO.setup(12, GPIO.OUT) GPIO.setup(13, GPIO.OUT) GPIO.output(12, GPIO.LOW) GPIO.output(13, GPIO.LOW) totalsteps = 0 for i in range(400): done = False counter = 0 average = 0 while not done: outData[slaveDesc.slaveAddr] = bytearray((0x00,0x00,0x00,0x00, )) for slaveDesc in master.getSlaveList(): slaveDesc.setOutData(outData[slaveDesc.slaveAddr]) handledSlaveDesc = master.run() if handledSlaveDesc: inData = handledSlaveDesc.getInData() if inData is not None: print(inData[3] + inData[2]*256) average = average + inData[3] + inData[2]*256 counter = counter + 1 if (counter > 9): done = True average = average / 10 if watchdog is not None: watchdog() print("AVERAGE: ", totalsteps, ", ", average, flush=True) forwarddata[totalsteps] = average; # now do a step GPIO.output(12, GPIO.HIGH) time.sleep(0.0001) GPIO.output(12, GPIO.LOW) time.sleep(1) totalsteps = totalsteps + 1 GPIO.output(13, GPIO.HIGH) for i in range(400): done = False counter = 0 average = 0 while not done: outData[slaveDesc.slaveAddr] = bytearray((0x00,0x00,0x00,0x00, )) for slaveDesc in master.getSlaveList(): slaveDesc.setOutData(outData[slaveDesc.slaveAddr]) handledSlaveDesc = master.run() if handledSlaveDesc: inData = handledSlaveDesc.getInData() if inData is not None: print(inData[3] + inData[2]*256) average = average + inData[3] + inData[2]*256 counter = counter + 1 if (counter > 9): done = True average = average / 10 if watchdog is not None: watchdog() print("AVERAGE: ", totalsteps, ", ", average, flush=True) backwardsdata[totalsteps] = average; # now do a step GPIO.output(12, GPIO.HIGH) time.sleep(0.0001) GPIO.output(12, GPIO.LOW) time.sleep(1) totalsteps = totalsteps - 1 for i in range( len(backwardsdata) ): print(i, forwarddata[i], backwardsdata[i], forwarddata[i] - backwardsdata[i]) except pyprofibus.ProfibusError as e: print("Terminating: %s" % str(e)) return 1 finally: GPIO.cleanup() if master: master.destroy() return 0 if __name__ == "__main__": import sys sys.exit(main()) -
I'm having a little trouble analyzing your data.
It looks like you are taking 3201 samples every revolution when I look at the .zip file you uploaded.
I didn't take a look at the Python code since I'm also not a Python expert.
Take a look at when your encoder flips over to it's minimum count and see that there seem to be ( to my eyes) 3201 samples between them.
That makes it a little difficult to analyze.
I'll take a look at your next data set after you upload it.
-
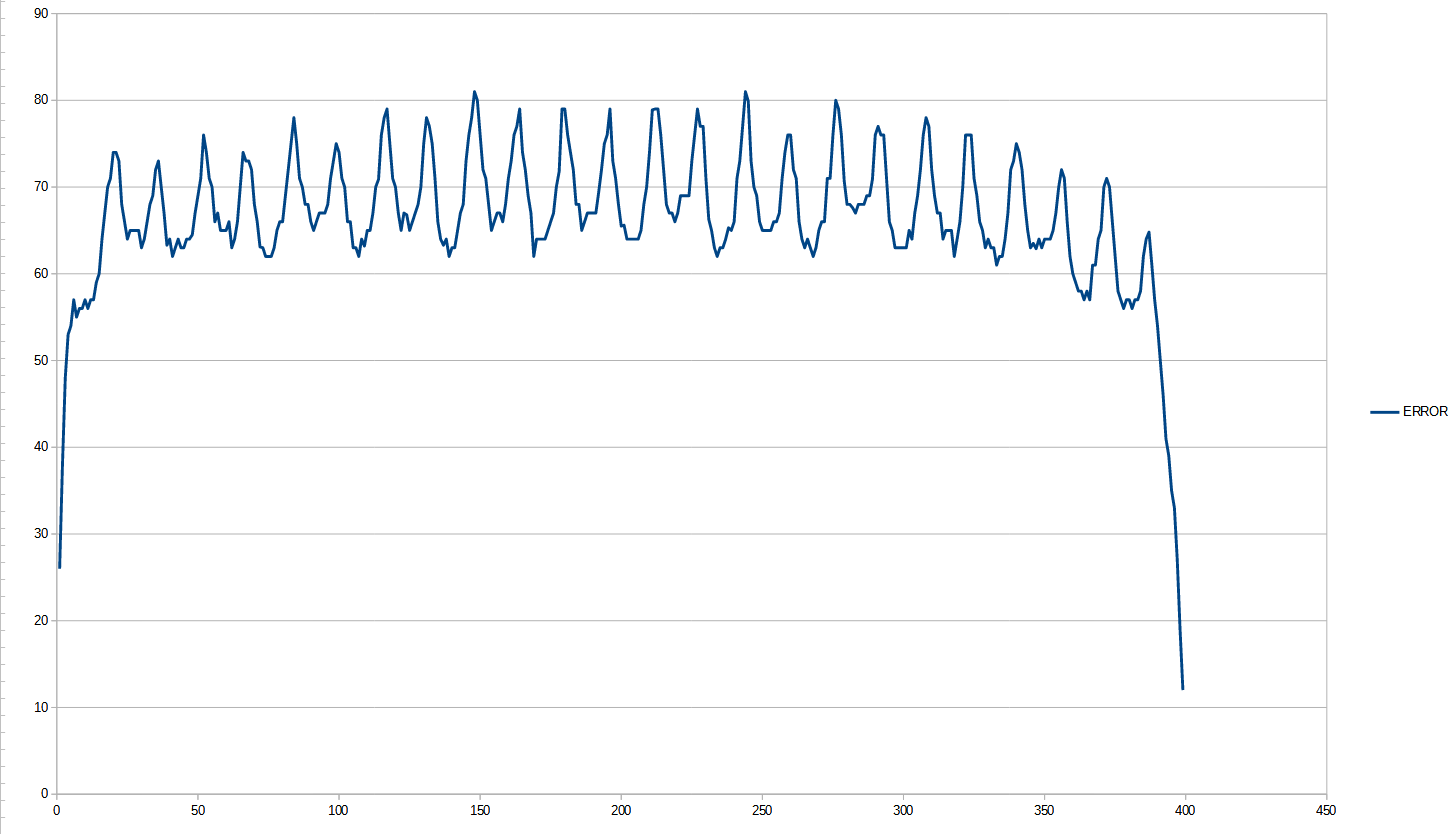
@alankilian going forward then backward and recording all steps was awesome suggestion ... data is ugly

-
It looks like you are taking 3201 samples every revolution when I look at the .zip file you uploaded.
the "multiturn" file is stepping for a while (whole night) going forward. encoder goes up to 65535 and then to 0 (it is absolute encoder) so it allow multiturn but records only positions inside one revolution
the "single turn" have 2 reasons to figure out it's full turn, one is to read the "similar" (20 less difference) position from the first one it reads when it start, and second reason is if it makes 400*32 steps (I assume 1/32 microstepping .9 degree motor ) .. first run it made 3199 steps in second 3200 steps. Motor is 1.8 degree and microstepping is 1/16 so 3200 steps is ok.
Now, you see "more" data, that's cause I do: Step, read encoder 10 times (output all 10), calc average of those 10 and display average value (add them all together and divide by 10). So for every step there is 11 rows in the txt file...
-
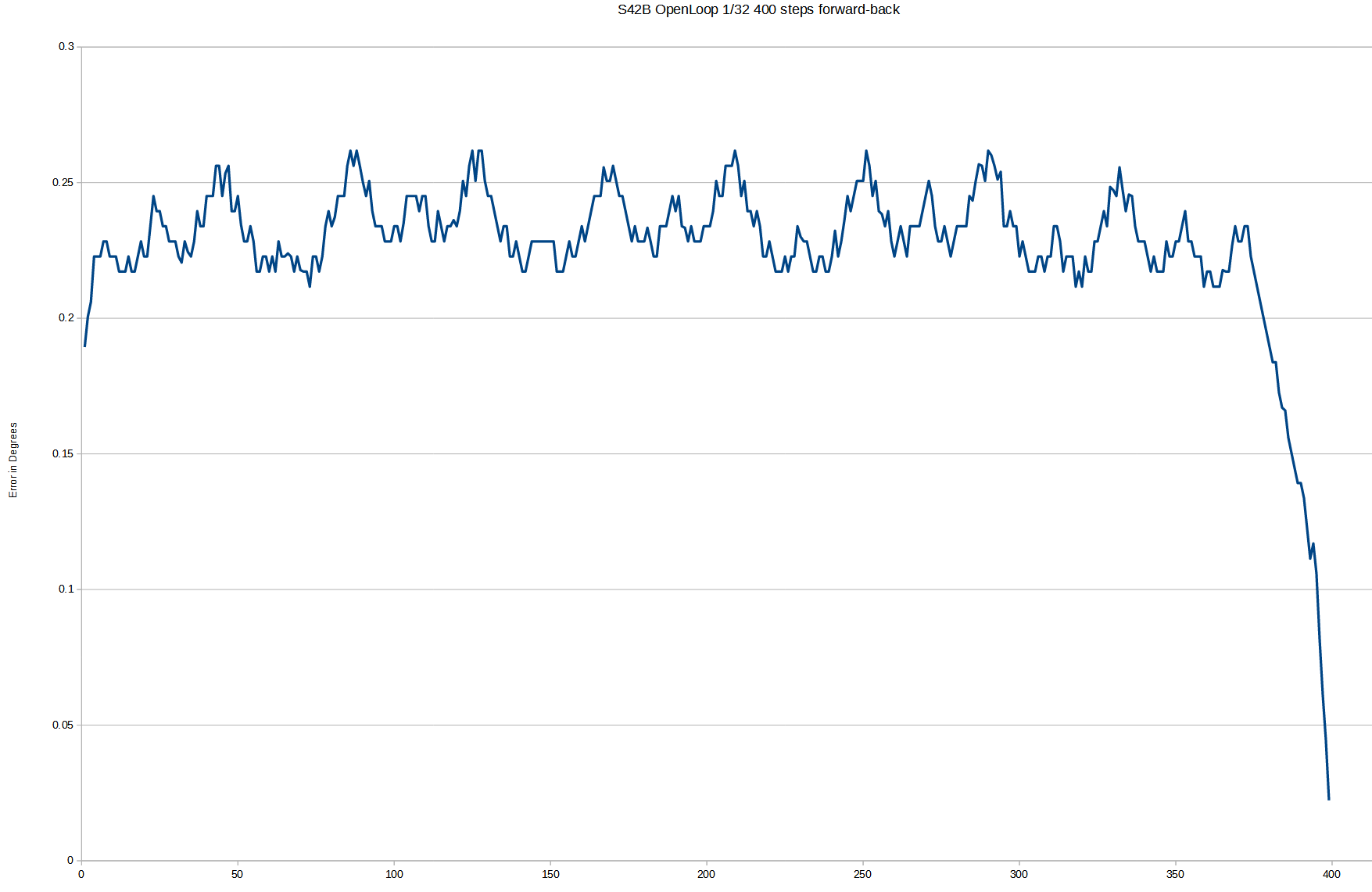
error goes from 60 to 80 or 0.33° to 0.44°
the span is 400 microsteps or 25 full steps so I'm assuming the full step positions are where the error is .33° and between steps the error goes up to .44°. I expected to see 50 peaks and not 25 as I expected that "half step" is nearly as precise as full step (as number of ppl and documents online state)
-
I'll use a stiff coupler now to see if that would make a difference...
-
raw data (the xls is few posts back)
-
S42B - same motor, open-loop mode, here we can see, I think the half stepping too...
-
@arhi Can you post your Python code for this?
I suspect there's an "off-by-one" somewhere and you're getting better results than you see in your graph.
I'm probably wrong, but if so, you might be happy.
-
This post is deleted! -
@alankilian said in stepper precision:
@arhi Can you post your Python code for this?
I suspect there's an "off-by-one" somewhere and you're getting better results than you see in your graph.
I'm probably wrong, but if so, you might be happy.
I hoped but it's not
 anyhow .. here it is:
anyhow .. here it is:#!/usr/bin/env python3 import pyprofibus import time import RPi.GPIO as GPIO def main(watchdog=None): master = None forwarddata = [] backwardsdata = [] #poserem se na jezik for i in range(410): forwarddata.append(0); backwardsdata.append(0); try: config = pyprofibus.PbConf.fromFile("arhi_readencoder.conf") master = config.makeDPM() outData = {} for slaveConf in config.slaveConfs: slaveDesc = slaveConf.makeDpSlaveDesc() master.addSlave(slaveDesc) outData[slaveDesc.slaveAddr] = bytearray((0x00, )) master.initialize() GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BCM) GPIO.setup(12, GPIO.OUT) GPIO.setup(13, GPIO.OUT) GPIO.output(12, GPIO.LOW) GPIO.output(13, GPIO.LOW) totalsteps = 0 for i in range(400): done = False counter = 0 average = 0 while not done: outData[slaveDesc.slaveAddr] = bytearray((0x00,0x00,0x00,0x00, )) for slaveDesc in master.getSlaveList(): slaveDesc.setOutData(outData[slaveDesc.slaveAddr]) handledSlaveDesc = master.run() if handledSlaveDesc: inData = handledSlaveDesc.getInData() if inData is not None: print(inData[3] + inData[2]*256) average = average + inData[3] + inData[2]*256 counter = counter + 1 if (counter > 9): done = True average = average / 10 if watchdog is not None: watchdog() print("AVERAGE: ", totalsteps, ", ", average, flush=True) forwarddata[totalsteps] = average; # now do a step GPIO.output(12, GPIO.HIGH) time.sleep(0.0001) GPIO.output(12, GPIO.LOW) time.sleep(1) totalsteps = totalsteps + 1 GPIO.output(13, GPIO.HIGH) for i in range(400): done = False counter = 0 average = 0 while not done: outData[slaveDesc.slaveAddr] = bytearray((0x00,0x00,0x00,0x00, )) for slaveDesc in master.getSlaveList(): slaveDesc.setOutData(outData[slaveDesc.slaveAddr]) handledSlaveDesc = master.run() if handledSlaveDesc: inData = handledSlaveDesc.getInData() if inData is not None: print(inData[3] + inData[2]*256) average = average + inData[3] + inData[2]*256 counter = counter + 1 if (counter > 9): done = True average = average / 10 if watchdog is not None: watchdog() print("AVERAGE: ", totalsteps, ", ", average, flush=True) backwardsdata[totalsteps] = average; # now do a step GPIO.output(12, GPIO.HIGH) time.sleep(0.0001) GPIO.output(12, GPIO.LOW) time.sleep(1) totalsteps = totalsteps - 1 for i in range( len(backwardsdata) ): print(i, forwarddata[i], backwardsdata[i], forwarddata[i] - backwardsdata[i]) except pyprofibus.ProfibusError as e: print("Terminating: %s" % str(e)) return 1 finally: GPIO.cleanup() if master: master.destroy() return 0 if __name__ == "__main__": import sys sys.exit(main())The "off by one" is imho "not a problem" as if you look at the printout ..
0 20828.0 0 20828.0 1 20835.0 20869.0 -34.0 2 20840.0 20876.0 -36.0 ... 398 23964.0 23972.0 -8.0 399 23972.0 23976.0 -4.0 400 0 23979.0 -23979.0you see that firs read is 20828.0, 0 - so going backwards I did not read backwards at all, and last read is 0, 23979.0 so going forward I didn't read that one ...
also you see the "end" going forward it goes up (last dataset, for the TMC driver it's reversed)
23964.0
23972.0then first read backwards (actually it was not stepped backwards yet that's position after last step forward)
23979.0 so larger than 23972and then it goes down again
23976.0
23972.0also, if you look how error is down to nothing when you just turn direction and how it rises... takes some 20+ steps in reverse for error to catch up the average values..
First step back the error is 0.02 degrees
-
I managed to get S42B v1.0 to work (no clue how any more), now it's running in closedloop mode too so waiting for results... interesting - I have no clue what microstepping it is running at, lcd configured 1/32 but what it is actually doing - no clue, will run the original one direction full circle after this back-forth finish
need to find my vallder (leadshine clone) .. dunno where I put the darn thing in this chaos